Counting Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
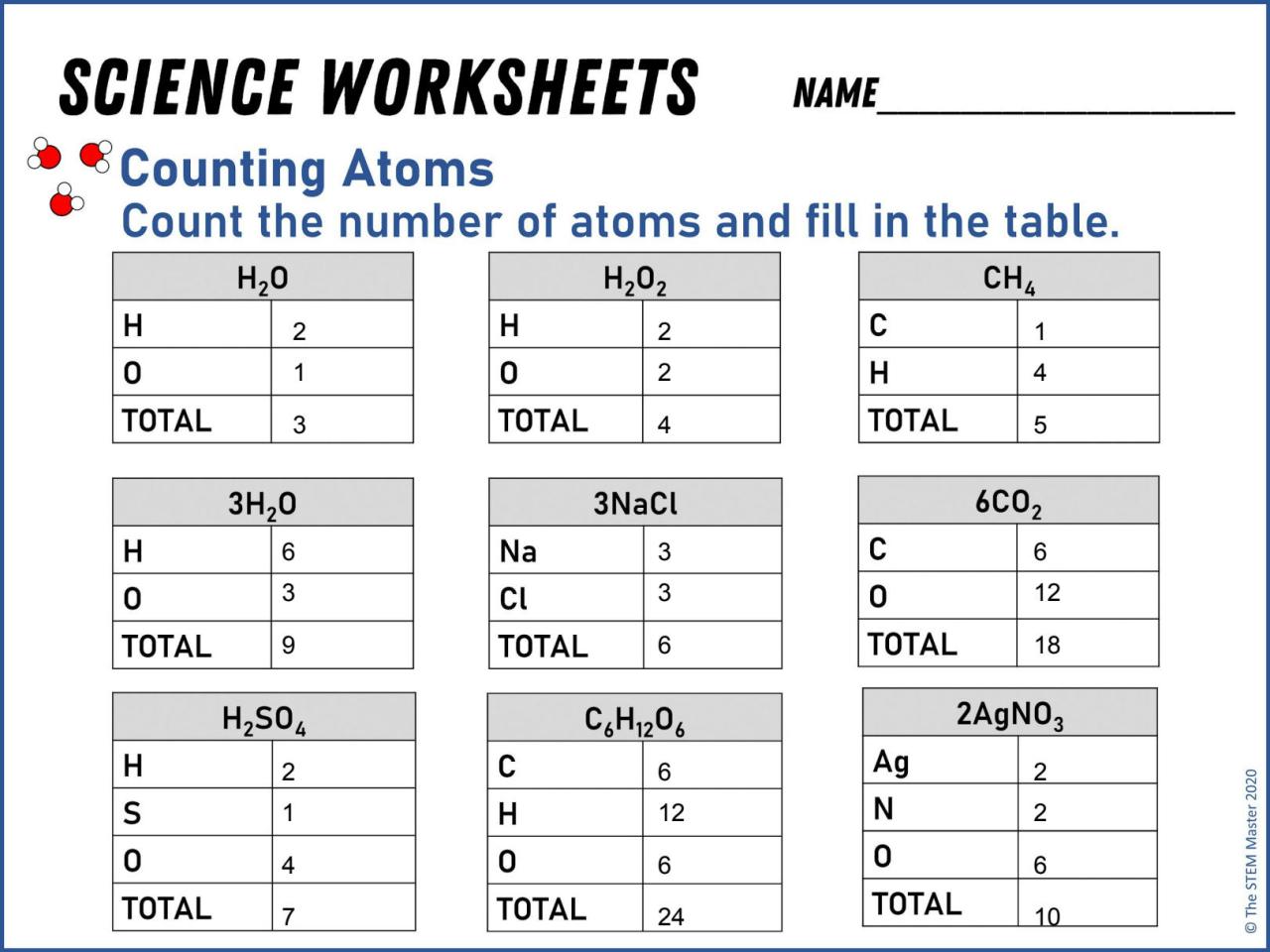
Counting atoms worksheet answer key – This worksheet provides a comprehensive guide to counting atoms in chemical formulas. It is an essential skill for understanding the composition of chemical compounds and their properties.
Counting atoms helps determine the molecular weight, empirical formula, and structural formula of a compound. It also enables the calculation of the number of moles of a substance present in a given sample.
Steps Involved in Counting Atoms in a Chemical Formula
- Identify the chemical formula of the compound.
- Determine the number of atoms of each element in the formula.
- Multiply the number of atoms by the subscript of each element.
- Add the number of atoms for each element to get the total number of atoms in the formula.
Examples and Practice Problems for Counting Atoms: Counting Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
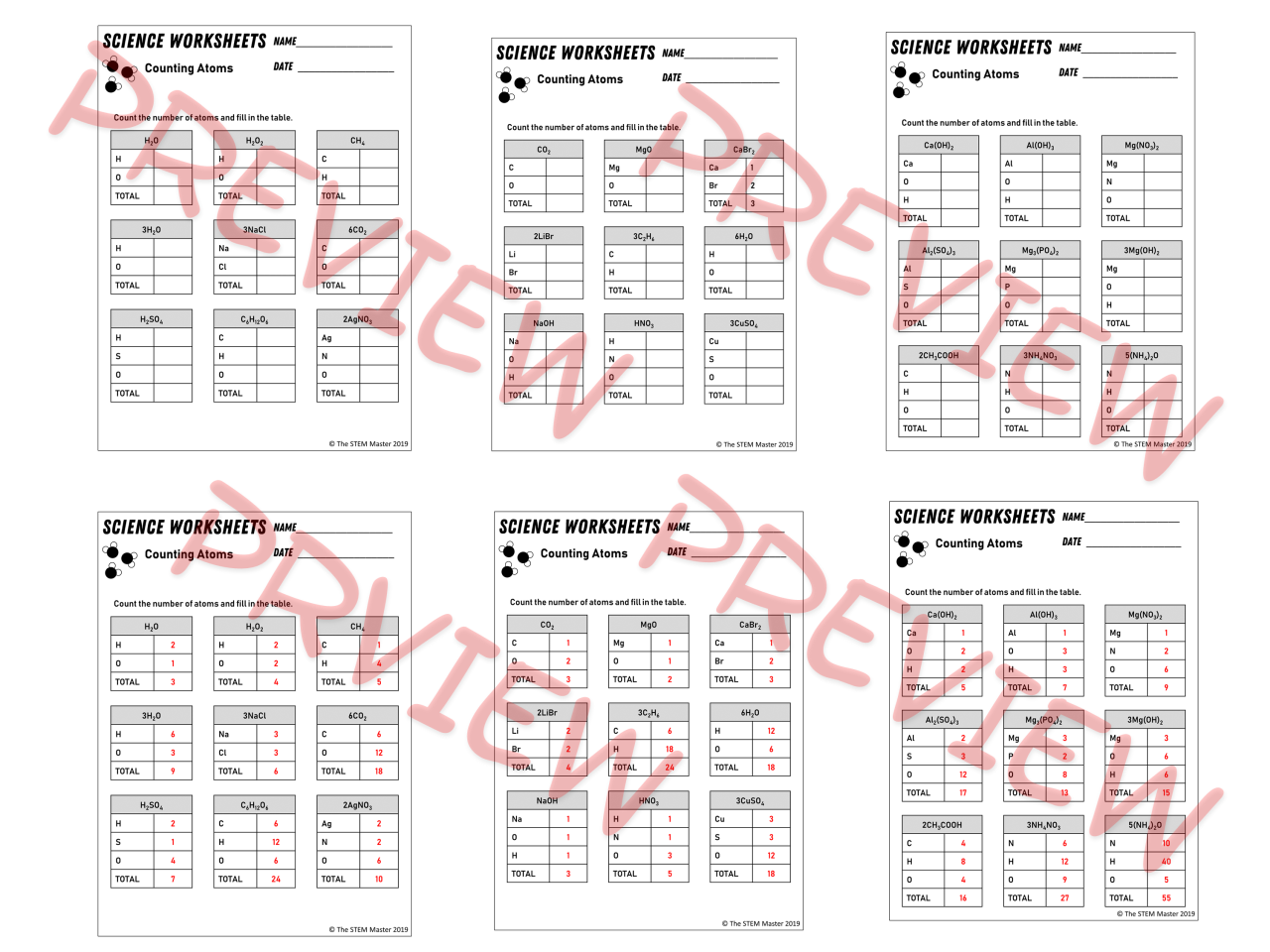
Counting atoms is a fundamental skill in chemistry. It allows us to determine the number of atoms of each element in a given compound, which is essential for understanding its properties and reactions. In this section, we will provide examples and practice problems to help you master the technique of counting atoms.
Table of Chemical Formulas and Atom Counts, Counting atoms worksheet answer key
The following table lists various chemical formulas and their corresponding atom counts:| Chemical Formula | Atom Counts ||—|—|| H 2O | 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom || NaCl | 1 sodium atom, 1 chlorine atom || CH 4| 1 carbon atom, 4 hydrogen atoms || C 6H 12O 6| 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, 6 oxygen atoms |
Step-by-Step Demonstration of Counting Atoms
To count the atoms in a chemical formula, follow these steps:
- Identify the chemical symbols for each element in the formula.
- For each element, count the number of atoms represented by its subscript. If there is no subscript, assume that there is one atom of that element.
- Multiply the number of atoms by the subscript for each element.
- Add up the total number of atoms for each element to get the total atom count.
For example, to count the atoms in the formula C 6H 12O 6, we would:
1. Identify the chemical symbols for each element
C, H, and O.
2. Count the number of atoms represented by the subscripts
6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms.
3. Multiply the number of atoms by the subscript for each element
6 x 1 = 6 carbon atoms, 12 x 1 = 12 hydrogen atoms, 6 x 1 = 6 oxygen atoms.
4. Add up the total number of atoms for each element to get the total atom count
6 + 12 + 6 = 24 atoms.
Practice Problems
1. Count the number of atoms in the following formula
NH 3
2. Count the number of carbon atoms in the following formula
C 12H 22O 11
3. Count the number of oxygen atoms in the following formula
Fe 2O 3
Helpful Answers
Why is counting atoms important in chemistry?
Counting atoms provides a foundation for understanding the composition and behavior of chemical substances. It allows us to determine the ratios of elements in compounds, balance chemical equations, and calculate various chemical properties.
How do I count atoms in a chemical formula?
To count atoms in a chemical formula, identify each element and its corresponding subscript. The subscript indicates the number of atoms of that element in the formula. For example, in H2O, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
What are some applications of counting atoms in chemistry?
Counting atoms has numerous applications, including balancing chemical equations, determining the limiting reactant in a reaction, calculating the molar mass of compounds, and understanding stoichiometry.